Use Cases
API Orchestration
What is API Orchestration?
API Orchestration is the process of coordinating multiple API calls and services to create complex, multi-step workflows that deliver comprehensive functionality to your applications. While traditional API gateways focus on simple request routing, API orchestration goes far beyond by managing intricate sequences of operations across multiple systems.
Think of it as the difference between a traffic light (simple routing) and a smart traffic management system (orchestration) that coordinates multiple intersections, manages traffic flow, and optimizes routes in real-time.
How API Orchestration Works
When an external system or user makes an API call, the orchestration layer doesn't just route to a single endpoint. Instead, it performs a sophisticated sequence of operations:
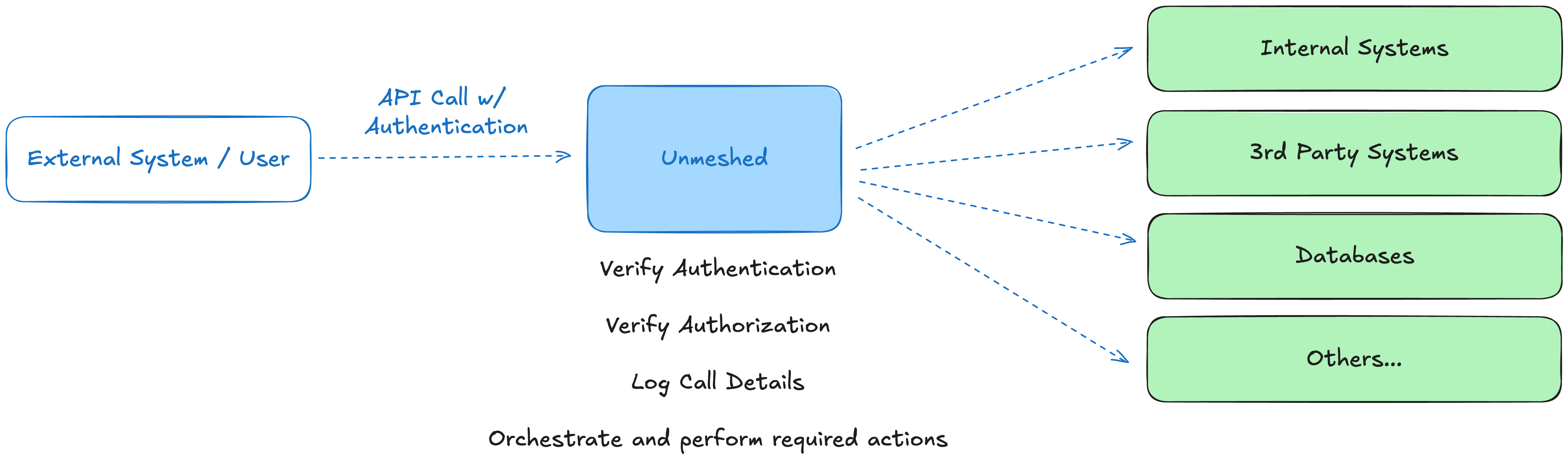
The Orchestration Process
- Authentication & Authorization: Verify the caller's identity and permissions
- Request Logging: Capture call details for monitoring and debugging
- Multi-System Coordination: Orchestrate actions across various backend systems:
- Internal Systems: Your organization's microservices and applications
- 3rd Party Systems: External APIs and services
- Databases: Data storage and retrieval operations
- Other Services: Additional systems and resources
Beyond Simple Routing
Unlike basic API gateways that route requests to a single destination, API orchestration:
- Aggregates Data: Combines information from multiple sources into a unified response
- Transforms Data: Converts data formats to match your application's requirements
- Manages Dependencies: Handles complex workflows where one operation depends on another
- Provides Resilience: Implements retry logic, fallback mechanisms, and error handling
- Optimizes Performance: Executes operations in parallel when possible, reducing overall response time
Real-World Example
Consider a user profile page that needs to display:
- User information from your user service
- Recent orders from your order management system
- Payment history from a third-party payment processor
- Recommendations from your ML service
Instead of making 4 separate API calls from your frontend, API orchestration handles all of this in a single, coordinated workflow, returning a complete, formatted response ready for your UI.
Implementing API Orchestration in Unmeshed
Unmeshed provides two key features for API orchestration:
Process Definitions
Implement your API functions using Process Definitions. These can leverage all supported step types:
- HTTP/REST calls
- GraphQL calls
- Scripting (Python or JavaScript)
- Switch Cases
- While Loops
- For Loops
- And more...
API Mapping
Use API Mappings to create endpoints that route to your process definitions.
Recommended Pattern
Create a single endpoint mapping that follows this pattern:
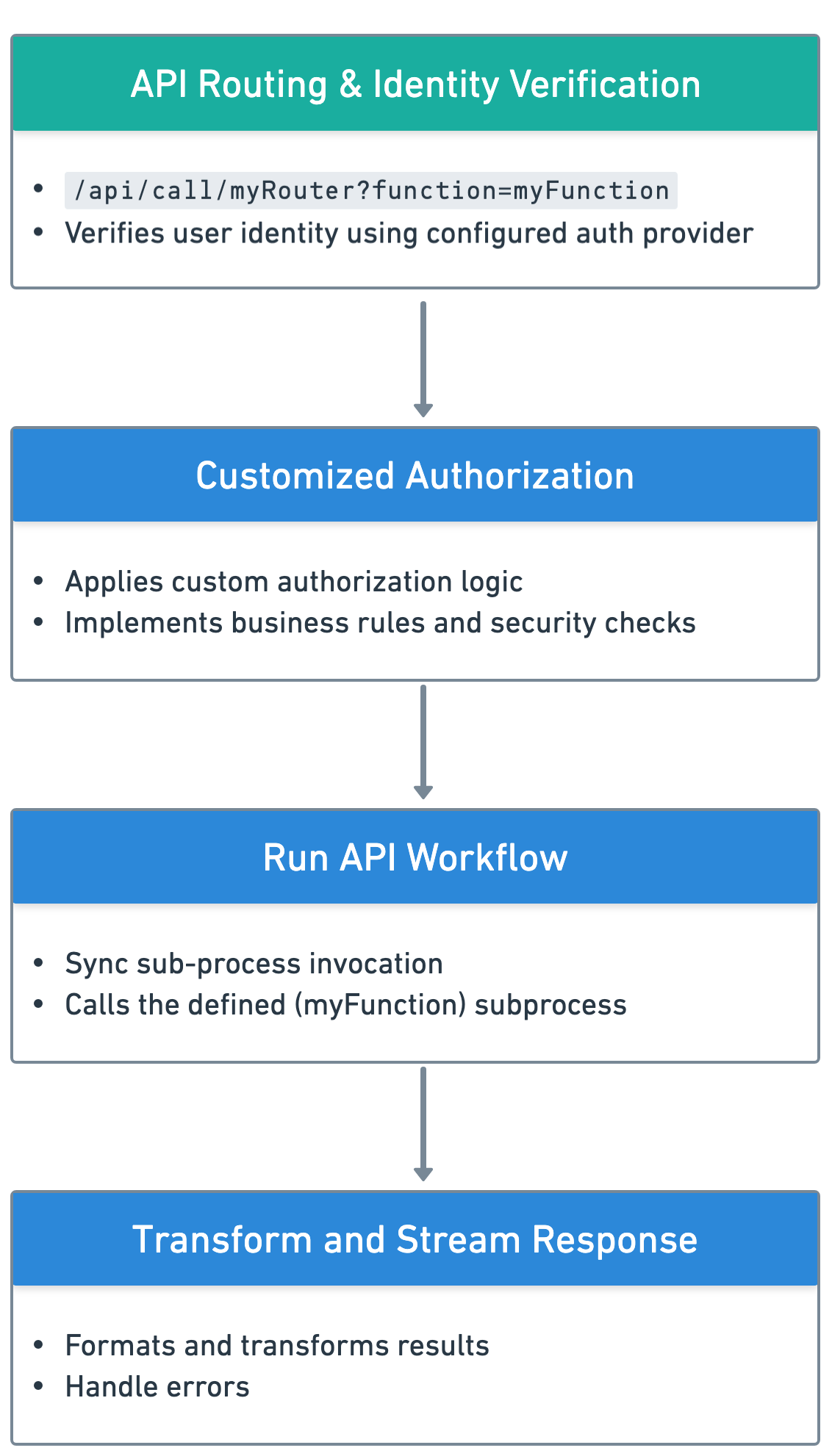
- Identify User: Extract user identity from authentication mechanism
- Authorize User: Apply rule-based authorization logic using any process definition features
- Call API Function: Invoke the required API function as a subprocess
Implementation Details
The single endpoint created via API mapping acts as your main router - similar to:
- Java: Web filters or interceptors
- Node.js: Express middleware
- Python: Django/Flask middleware
- .NET: Action filters or middleware
This main router can contain common logic for all API calls, functioning like a filter in any programming language.
Example Router Implementation
Let's examine a real-world example of the apiCall process that implements the recommended router pattern:
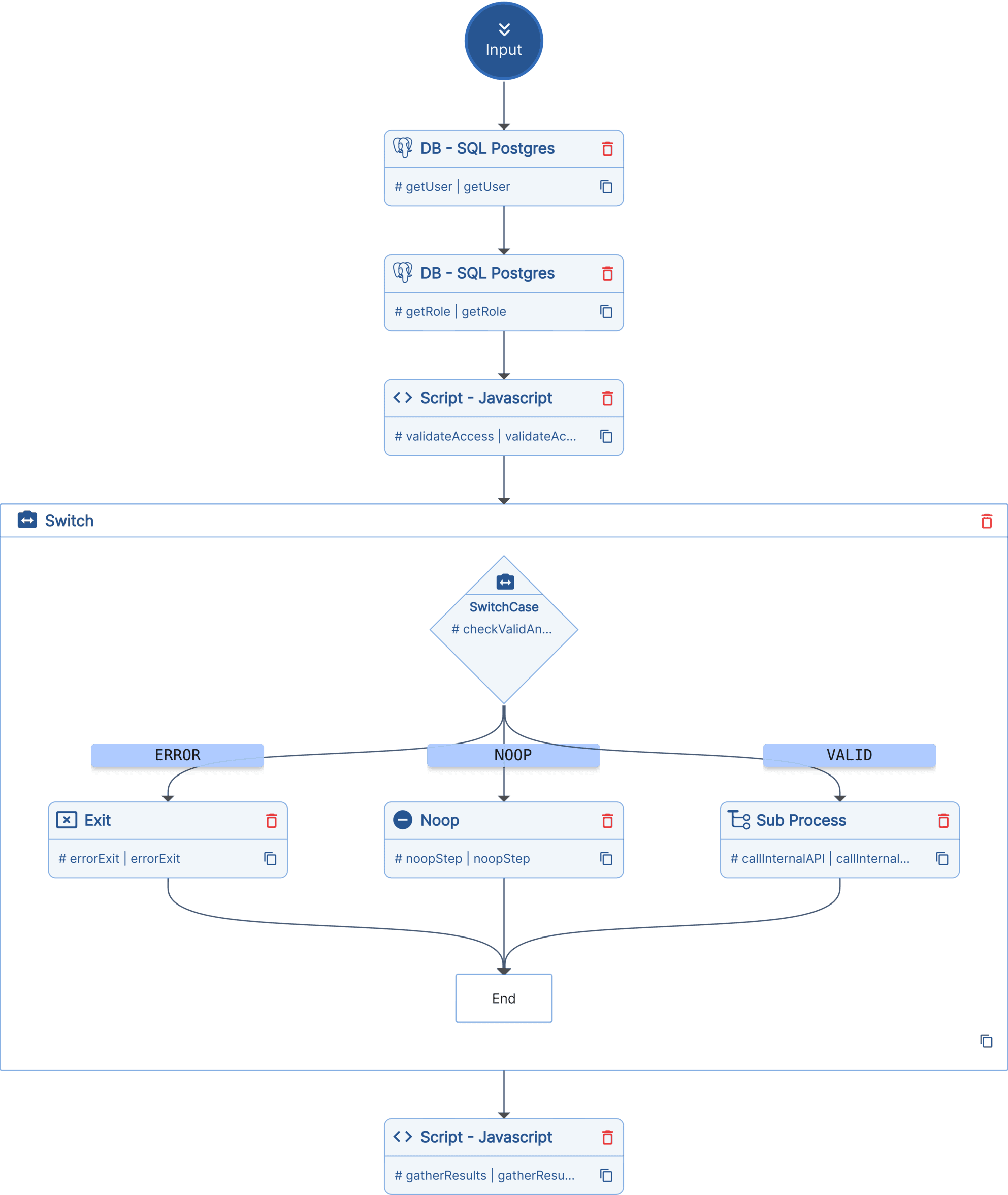
Process Flow
- getUser: Queries PostgreSQL to fetch user details using the authenticated user's email
- getRole: Retrieves user's team role and permissions from the database
- validateAccess: JavaScript script that implements authorization logic:
- Checks if the requested API function is allowed
- Validates role-based permissions (ADMIN, READONLY, etc.)
- Returns authorization decision
- checkValidAndRun: Switch statement that routes based on authorization:
- ERROR: Exits with 400 status for unauthorized requests
- NOOP: Returns success for health checks
- VALID: Calls the requested API function as a subprocess
- gatherResults: Final JavaScript step that formats the response
Key Features Demonstrated
- Authentication: Uses
{{context.authClaims.email}}from OAuth2.0 - Authorization: Role-based access control with business logic
- Subprocess Calls: Dynamically invokes different API functions
- Error Handling: Graceful error responses with proper HTTP status codes
- Response Transformation: Formats data for consistent API responses
This pattern centralizes authentication, authorization, and common logic while allowing flexible API function execution.